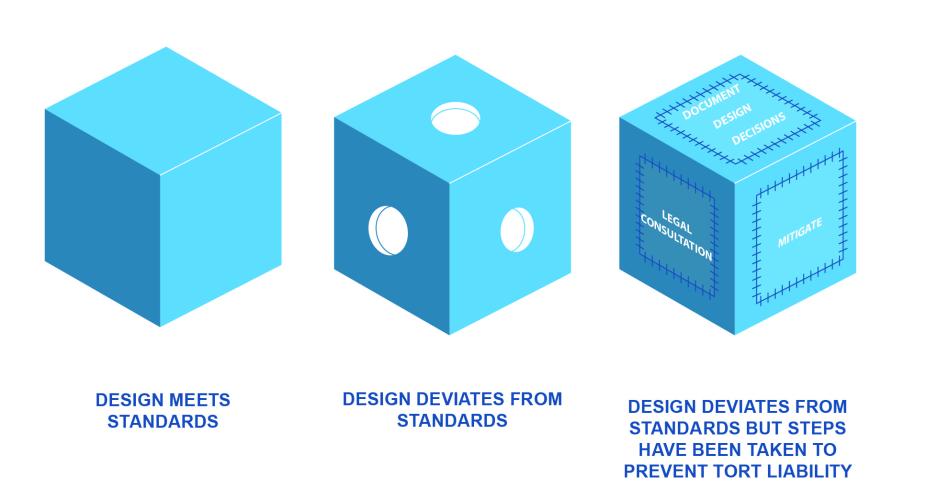
Liability is sometimes cited as a reason for not deviating from maximum standards in street design. Tort liability occurs when a court finds an agency responsible for injuries caused by negligent street design. Tort liability cases either argue that 1) an agency deviated from adopted practice or standards (Mandatory Duty), or 2) that a designer deviated from adopted practices and failed to exercise a standard of care. Traffic engineers must fully understand their agency’s liability responsibility and discretionary immunity in applying flexibility in street design. Engineers must be diligent in documenting their rationale for application of design flexibility, particularly when they deviate from adopted standards.
The following recommendations are adopted from a presentation presented to NACTO in 2014 by Jeanne Scherer, Deputy Chief Counsel, Caltrans:
- Develop a flexible design review and approval process and follow it every time. If flexible design results in accepted alternative designs based on engineering judgement, and has been properly approved, exposure to liability should not be increased.
- Memorialize design decisions. Document what was designed and why so it can easily be explained to others. Document standard design features selected and if deviation is necessary, explain why. Document throughout the design process the safety concerns that were addressed.
- Know the rationale and research behind design standards. To make informed design decisions, learn why the standards are what they are. Avoid making decisions in a vacuum; use reference material; seek out other subject matter experts.
- Mitigate if necessary. If alternate designs results in elimination or modification of a standard safety feature, mitigate the situation. For example, lower speed limits, provide special warning signs, increase lighting.
- Document and have approved engineering judgements when varying from published guidelines or when no guidelines are available. Retain your documentation.
- Consult with legal counsel for guidance on documents needed to establish defenses.
Body